Definition
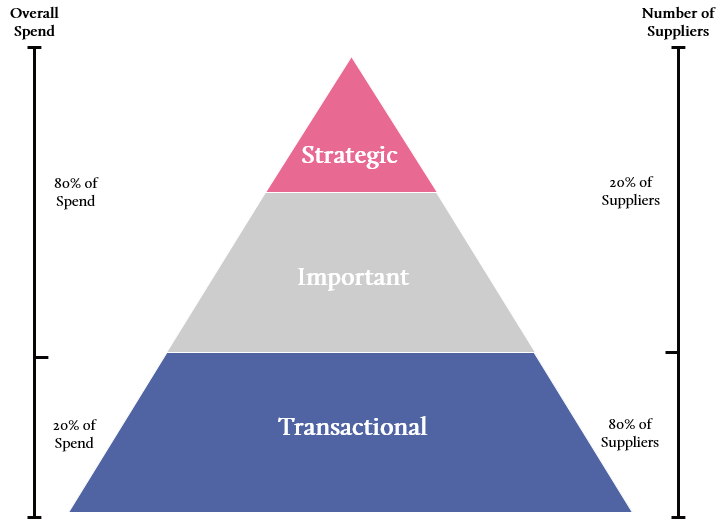
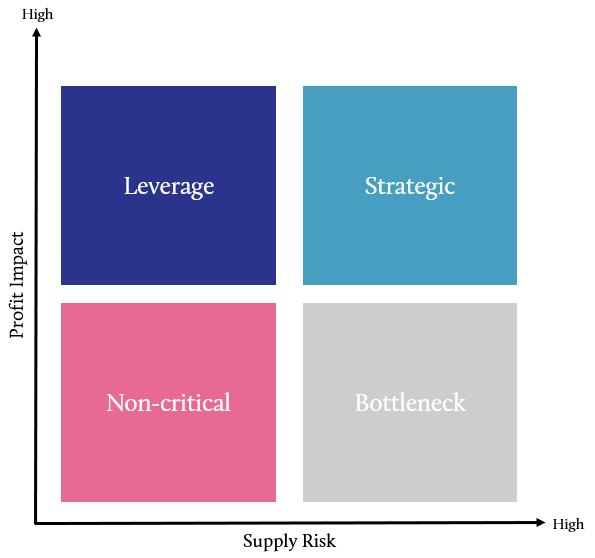
Supplier Segmentation, or Supplier Positioning, refers to the process of classifying suppliers in terms of their importance to the organization. It is an integral part of a Supplier Management program that helps define the resources, processes and procedures that are applied to a supplier relationship.
Templates
Need more help? Have a request? Please drop us a line...